Confined Space
Definition

Confined space is defined as a location that is an enclosed or partially enclosed space that is not primarily designed or intended for human occupancy.
- It has a restricted entrance or exit by way of location. As per Punjab Factory Rule-64 size should not be less that 40 cm X 30 cm for rectangular opening and 40 cm in diameter for circular opening.
- Can represent a risk to workers (any of the following):
- its design, construction, location or atmosphere,
- the materials or substances in it,
- work activities being carried out in it, or the
- mechanical, process and safety hazards present.
For instances, Process vessels, storage tanks, columns, boilers, pipes, ducts, sewers, which carry process fluids or gases. Any excavation of depth of 1.2 meters or above, entry onto tank floating roof, when the roof is 3 meters or more down from top of tank.
Hazard

- Poor Air Quality (O2 – 21% ± 2.5%, Min-19.5% & Max-23.5%): The atmosphere might contain insufficient amount of oxygen or a poisonous substance that could make the worker ill or even cause the worker to lose consciousness.
- Presence of Toxic air (anaerobic bacteria) i.e. CH4, CO, etc.
- Illumination: It has dark areas inside it which requires proper illumination prior work commences.
- Process related Hazard: Chemicals getting deposited on walls during cleaning of tanks after 2-4 years.
- Fire hazards: There may be an explosive/flammable atmosphere due to flammable liquids and gases which may catch fire or explode.
- Temperature extremes including atmospheric and surface.
- Uncontrolled energy including electrical shock. Eg: valve at tanks.
- Noise.
- Shifting or collapse of bulk materials.
- Visibility.
- Biological hazards.
Variability & Unpredictability is why the hazard assessment is extremely important and must be taken very seriously each and every time one is done.

- The entrance/exit of the confined space night does not allow the worker to get out in time should there be a flood or collapse of free-flowing solid.
- Natural Ventilation alone will not be sufficient to maintain breathable quality air.
The interior configuration of the confined space does not allow easy movement of air within it. - Condition can change very easily and quickly.
- Self-Rescue by the worker is more difficult.
- Work activities may introduce hazards do not present initially.
Preparation to enter Confined Space
To remember things each time a worker plans to enter any workspace, the worker should determine if that workspace is considered a confined space. Be sure the confined space hazard assessment, control program and toolbox talks has been followed.
Before entering any confined space, a trained and experienced person (i.e. Safety Officer, Supervisor, Contractor, etc.) should identify and evaluate all the potential hazards within the confined space and following points are to be make sure:
- Permit-to-Work based.
- Air quality should be normal.
- Safety watch keeper as personal (stand by with First Aid).
- Toxic atmosphere is eliminated.
- Ventilation provision.
- Lighting provision.
- Continuous Air Monitoring.
- PPEs – SAR, SCABA, Helmet, Fire control equipment.
- Communication device/protocol.
- Rescue equipment.
- Insulation Board.
- Toolbox Talk prior entry.
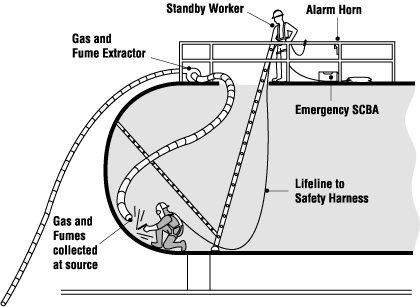
How is air quality maintained in Confined Space?
Natural ventilation is usually not reliable and not sufficient to maintain the air quality. Mechanical ventilation (blowers, fans, etc.) is usually necessary to maintain air quality.
- Mechanical ventilation (use of blower): If mechanical ventilation is provided, there should be a warning system in place to immediately notify the worker in the event of a hazard or a failure in the
ventilation equipment. - Direct of proper suction/clean air: Care should be taken to make sure the air being provided by the ventilation system to the confined space is “clean”.
- Supply of O2/ fresh air: Do not substitute oxygen for fresh air. Increasing the oxygen content will significantly increase the risk of fire and explosion.
- The use of mechanical ventilation should be noted on the entry permit.
Likelihoods during work in Confined Space
Anyone working in a confined space must be constantly alert for a changing condition within the confined space. There should be warning signs to prevent unauthorized entry.
Another worker, safety watch, standby is to be posted outside the confined space and continuously monitors the workers inside the confined space.
- Maintain constant communication with the worker in the confined space.
- Calls for emergency assistance immediately if an emergency occurs.
- No confined space should be closed off until it has been verified that no person is inside it.
- After exiting confined space, the time of exit should be noted on the entry permit.
- Immediately available to provide non-entry emergency assistance when needed.
- Monitors the confined space and surrounding area and is on the look-out for dangerous conditions.

Ans: If properly ventilated, gas test readings are satisfactory, properly barricaded and warning signs are posted, trained standby man is present with log sheet, sufficient lighting and low voltage electricity (24V – 110V), proper means of communication, locked and tagged out, if necessary, lifeline and man retrieval system, if necessary, etc.
Que 3: Who is a confined space attendant?
Ans: He is one who is aware of the confined space hazards and knows how to react if anything goes wrong, able to maintain confined space entry log sheet, etc.
Que 4: What are the hazards in a confined space?
Ans: Oxygen deficiency or enrichment, present of toxic or flammable gases, chemical hazard, fire hazard, fall of materials, fall hazards, electrocution, dust, sound, heat or cold, caught in between moving parts of equipment’s, engulfment, etc.
Que 5: What are the duties of a confined space attendant?
Ans: He is responsible for the safety of entrants, should be present whenever people are working in confined space, maintain update entry log sheet, maintain continuous communication with entrants and monitor conditions in the confined space to ensure a safe working atmosphere, prevent unauthorized entry of personnel, initiate alarm for help if needed, evacuation the entrants if prevent unauthorized entry of personnel, initiate alarm for help if needed, evacuate the entrants if personnel if necessary, etc.
Que 6: Give some examples of Confined Space?
Ans: Pipes, Vessels, Tanks, Boilers & Tubes areas, Silos, Trenches & Excavation deeper then 4 feet, Sludge pits, Duct works, etc.
Que 7: Name one hazardous job in a Confined Space?
Ans: Welding, Grinding, Chemical cleaning, use of gas cutting set, erection of materials.

