How Electric Vehicle works?
Electric vehicles (EVs) operate on a different propulsion system than traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. They use electricity stored in batteries to power an electric motor, which drives the wheels. Here is how electric vehicles work, lets start with its components.

Components of an Electric Vehicle:
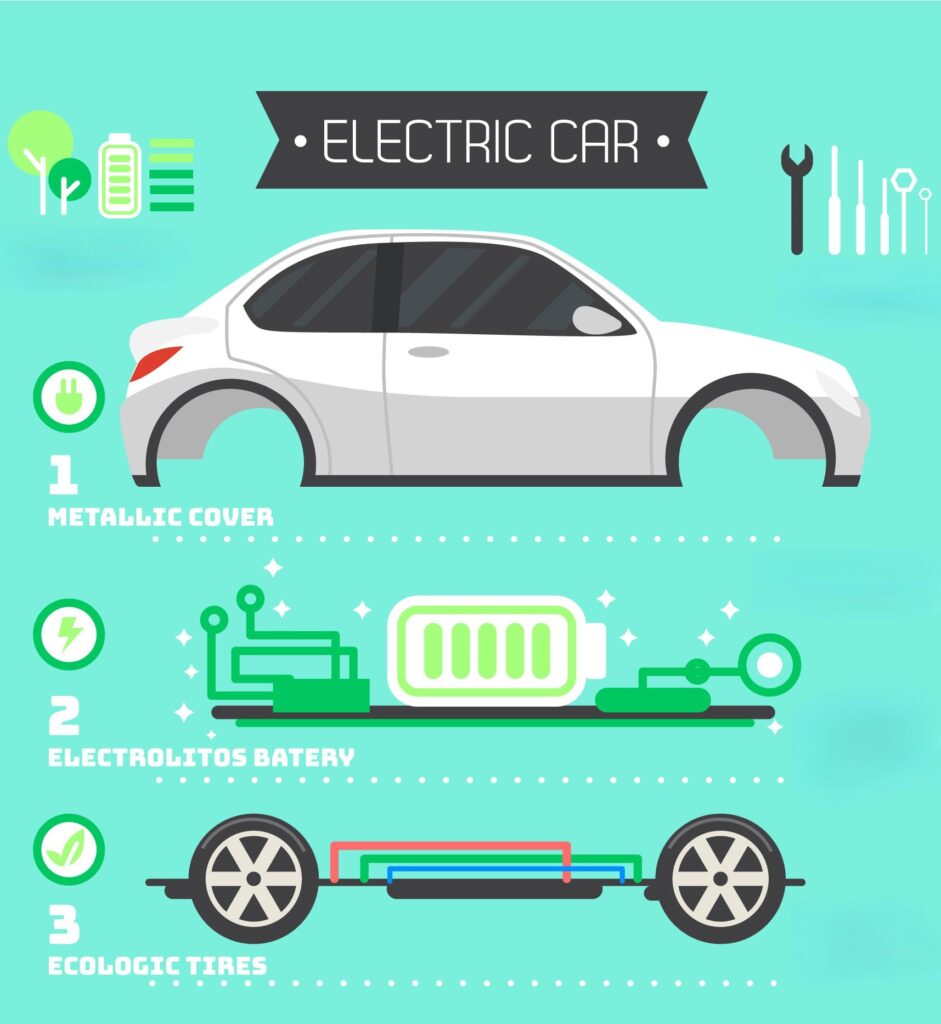
a) Battery Pack.
b) Electric Motor.
c) Power Electronics.
d) Charging Port.
a) Battery Pack:
- The battery pack is the heart of an electric vehicle. It stores electrical energy in chemical form and provides power to the electric motor.
- Most modern EVs use Lithium-ion batteries due to their high energy density and relatively light weight.

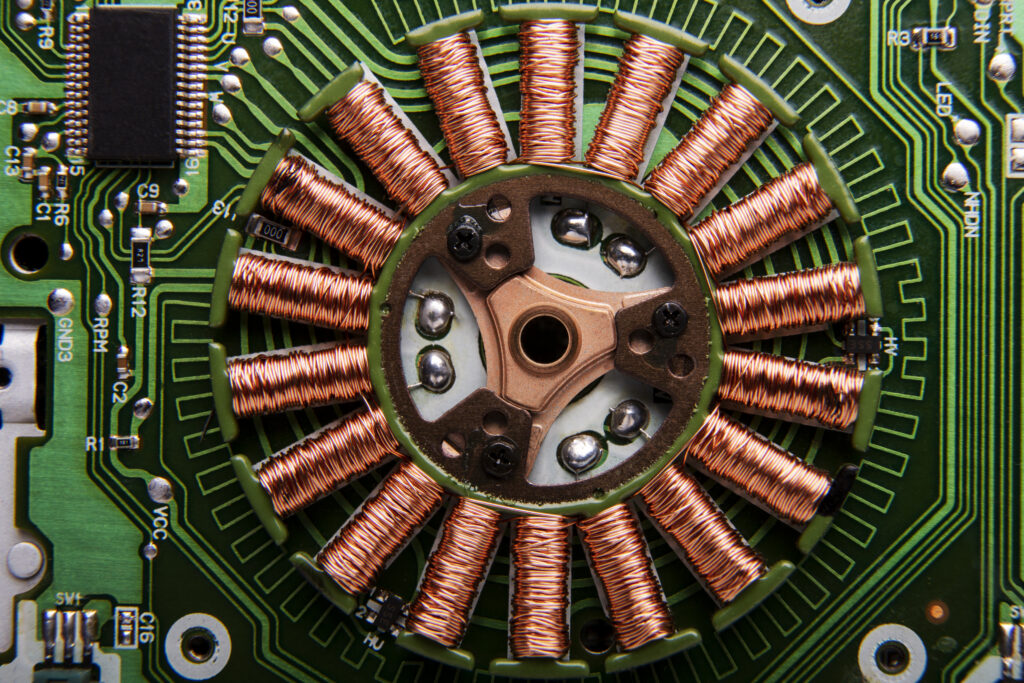
b) Electric Motor:
- The electric motor is responsible for converting electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to drive the vehicle.
- There are various types of electric motors used in EVs, including AC induction motors, permanent magnet motors and synchronous motors.

c) Power Electronics:
- Power electronics control the flow of electricity between the battery and the electric motor. They manage the speed, torque and direction of the motor.
- Power electronics components include inverter, converter and motor controllers.
d) Charging Port:
- The charging port allows the EV to connect to an external power source for recharging the battery.
- EVs can be charged using different types of charging stations, including home chargers, public chargers and fast chargers.
Electric Vehicle’s work
a) Charging the Battery.
b) Storing Energy.
c) Electric Motor Operation.
d) Regenerative Braking.
e) Driving the Vehicle.
f) Vehicle Control System.
g) Monitoring & Optimization.
a) Charging the Battery:
- Electric vehicles are charged by plugging them into a power source, such as a wall outlet or a charging station.
- The onboard charger converts AC power from the grid into DC power to charge the battery.
b) Storing Energy:
- The electricity from the charging source is stored in the battery pack, where it is converted into chemical energy through a series of electrochemical reactions.
- The Battery Management System (BMS) monitors and manages the state of charge, temperature and health of the battery cells.
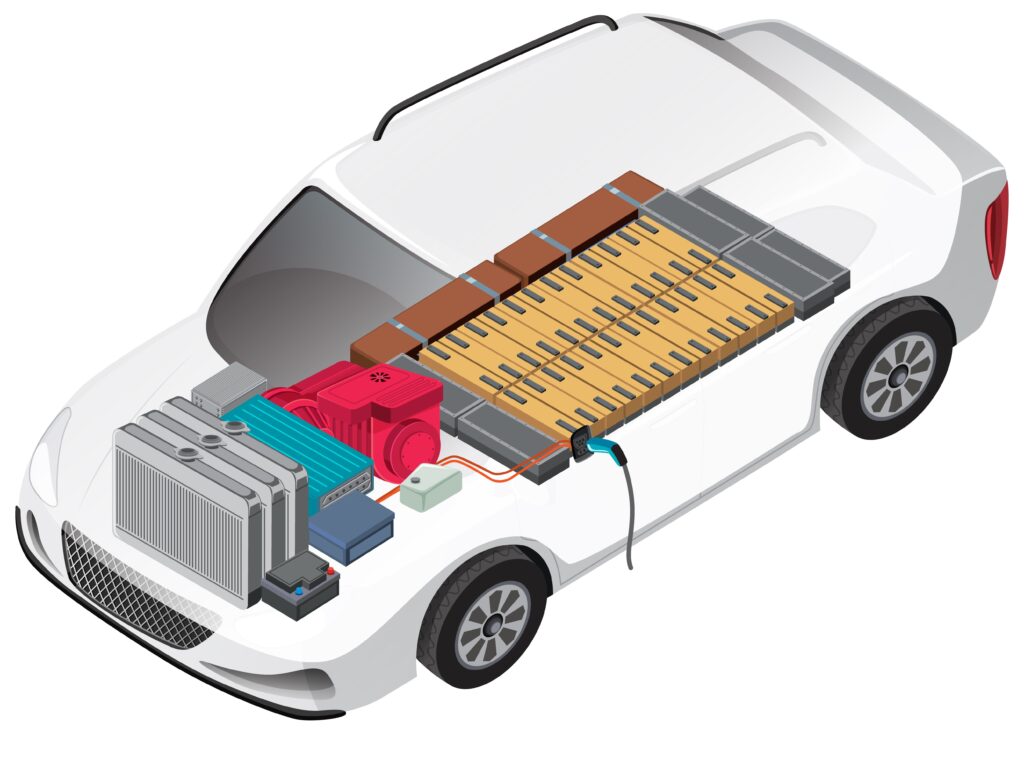
c) Electric Motor Operation:
- When the driver activates the accelerator pedal, the power electronics control the flow of electricity from the battery to the electric motor.
- The electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, generating torque to drive the wheels.
d) Regenerative Braking:
- During braking or deceleration, electric vehicles utilize regenerative braking to capture kinetic energy and convert it back into electrical energy.
- The electric motor acts as a generator, producing electricity that is fed back into the battery for storage.
e) Driving the Vehicle:
- The electric motor drives the wheels, providing smooth and quiet acceleration.
- EVs typically have a single-speed transmission, simplifying the drivetrain and improving efficiency.

f) Vehicle Control Systems:
- Various control systems, including traction control, stability control and brake-by-wire system, ensure safe and efficient operation of the vehicle.
- These systems use sensors and actuators to monitor and adjust vehicle performance in real-time.
g) Monitoring and Optimization:
- Advanced EVs may feature smart systems that optimize energy usage, such as predictive energy management and route planning based on traffic and topography.
- These systems help maximize range and efficiency while minimizing energy consumption.